The Roller Coaster of Oil Prices
Article
Sep 13, 2024
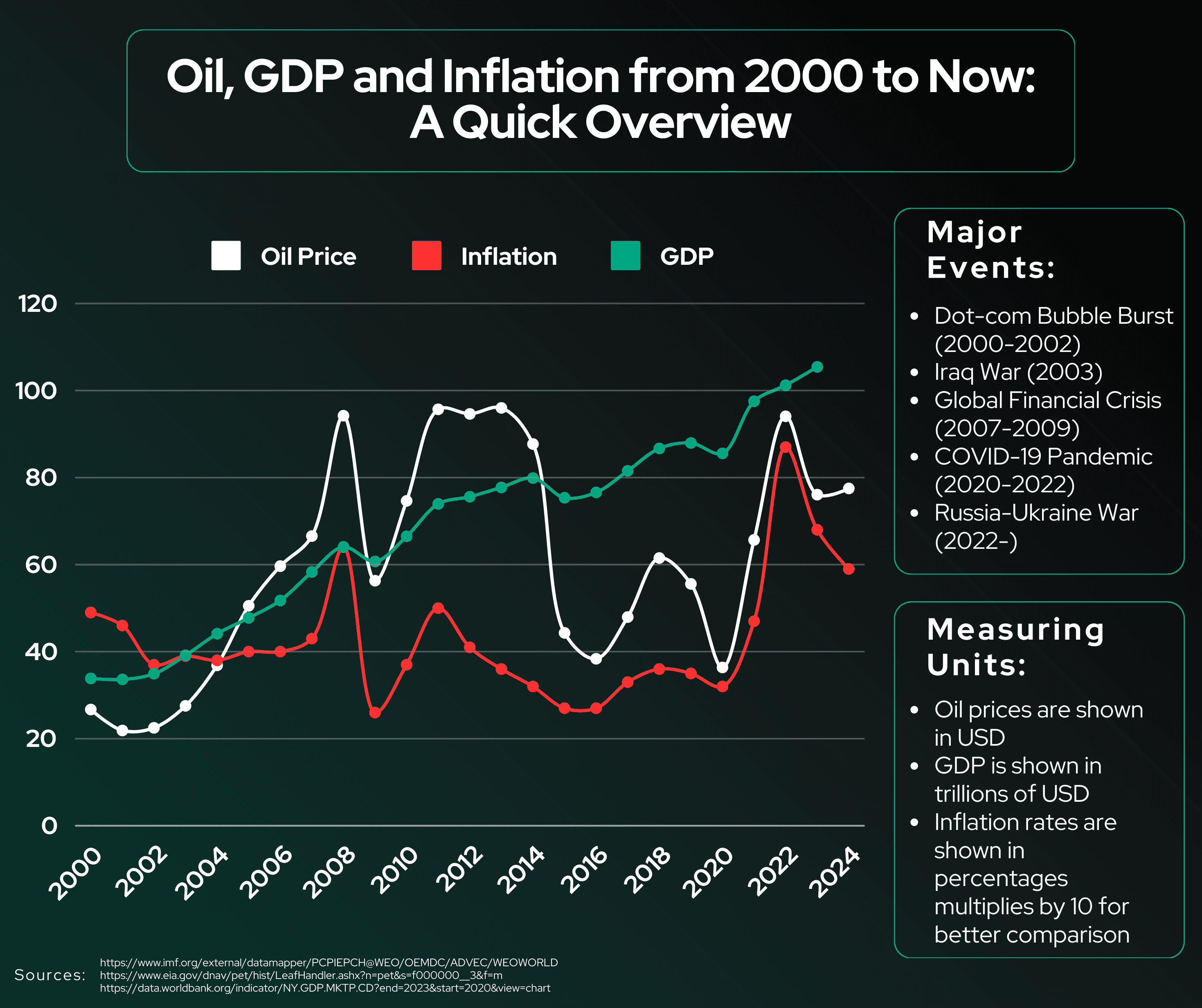
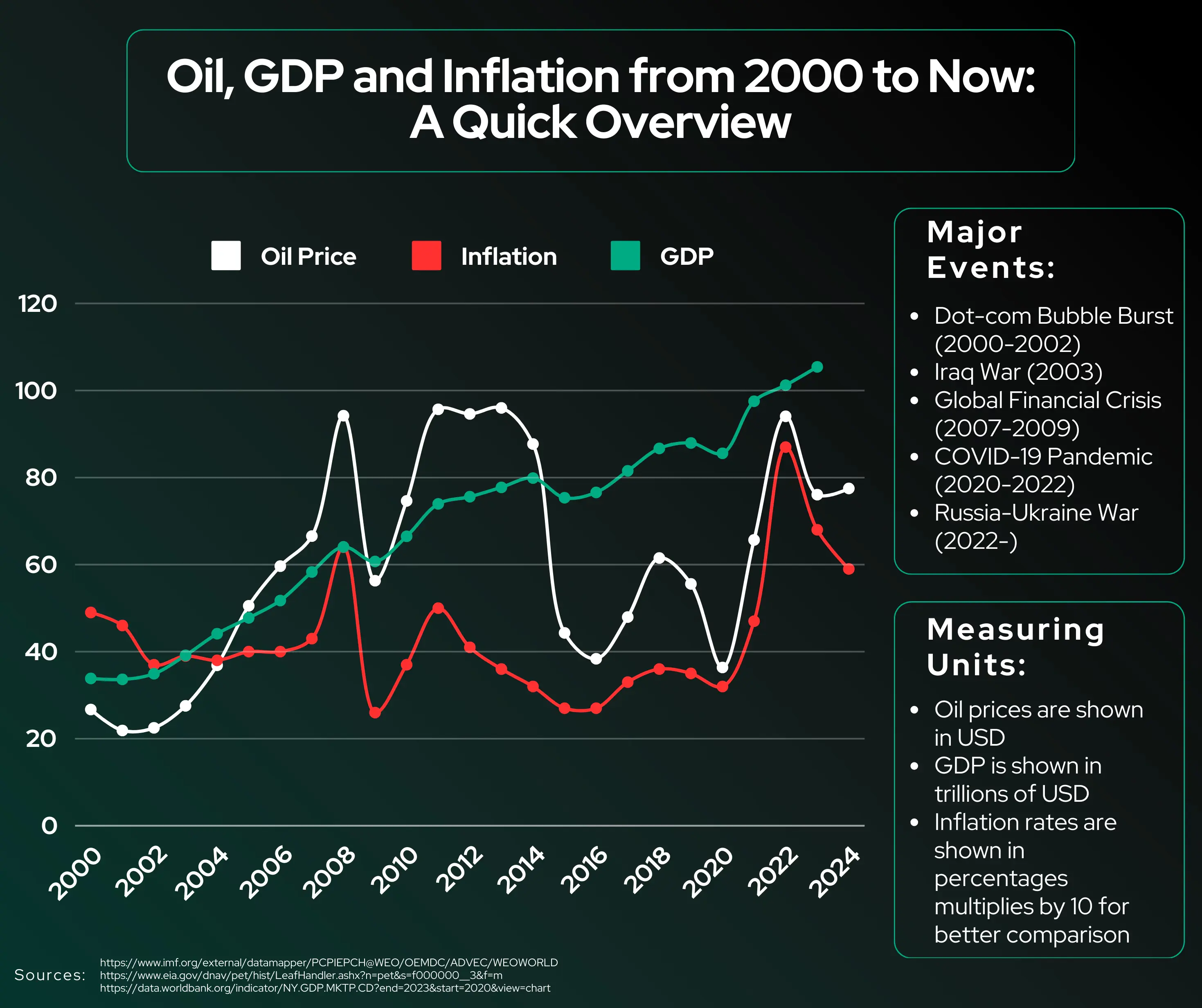
Oil prices are known to fluctuate frequently and drastically. These changes mimic the excitement of a roller coaster, but their unpredictability is not always a fun ride for consumers, businesses, or investors. However, in understanding where these fluctuations may come from, it makes predicting when these drastic changes may occur much easier.
OPEC’s Control over Supply
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, known by the acronym OPEC, consists of 12 countries (five in the Middle East, six in Africa, and one in South America), and controls around 80% of the world’s oil reserves. When OPEC decides to make less oil, there may not be enough supply to meet the demand. It is because of this decision that the price of oil then rises. However, if they decide to make more oil, the supply may then exceed the demand, thus causing the price of oil to go down.
This doesn't just affect oil, but also the economies of countries that depend on importing it. When there are tensions between countries, civil unrest, or political conflicts, oil prices can change drastically as well. In 2008, for example, when there was high political conflict and tension in the Middle East, oil prices hit a historic spike.
Natural Disasters and price shocks
Natural disasters can also disrupt oil production and cause the prices to fluctuate drastically. Such was true in 2005, when Hurricane Katrina stopped 20% of the United States’ oil supply. This was because of the hurricane hitting the Outer Continental Shelf in the Gulf of Mexico, which is a major site of oil production for the nation. In hitting that area, Hurricane Katrina damaged a total of 13 drilling rigs and 67 platforms, either completely destroying them or causing extensive damage.
The flooding of the Mississippi River in 2011 also had a notable impact on oil production. Eleven refineries were in the path of the flood water from the Mississippi River, which would majorly disrupt the normal operations for the refineries, even if the flood water did not hit them directly. The disruption of these refineries would then cause oil prices to rise.
The impact of COVID-19 on oil prices
The COVID-19 pandemic dramatically impacted oil prices. Shutdowns caused demand destruction, in which the demand plunged and nearly disappeared, causing oil prices to drop. However, as economies reopened, demand increased, and prices rose again. This relationship between supply and demand is a fundamental driver of oil price changes, and in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic and global shutdowns, these prices fluctuated intensely.
Production costs
The price of oil can go up and down for many different reasons. If big countries like China, the United States, or countries in the European Union aren't using as much oil, the prices can drop. If cheap sources, like oil from the Middle East, run out, more expensive options, like oil from Canada, would be used. Using the more expensive option would then, of course, make the price of oil rise. More expensive production methods raise prices, while storage levels in key locations can affect supply and pricing.
There are many factors that influence changes oil prices, and while some of them can be predicted with a degree of certainty, other are impossible to foresee. It is also important to note that most fluctuations of the oil prices are a result of the combined effects of several different factors, which makes them even more challenging to accurately anticipate.
On this page